

Bank statement verification is the process of confirming the accuracy and authenticity of an entity’s bank statements. This crucial practice helps determine that a statement is genuine, free from alterations, and corroborates other financial records. Thorough bank statement verification is a critical risk management measure for businesses, lending institutions, accounting firms, and individuals when evaluating loans, investment opportunities, audits, and more. Confirming bank statements are valid and match transactions is an integral part of due diligence across industries to mitigate fraud and ensure financial integrity. Streamline your accounting processes with AI – details inside our eBook!
 what is bank statement verification" width="1280" height="800" />
what is bank statement verification" width="1280" height="800" />
Bank statement verification is the process of authenticating the accuracy and authenticity of a bank account statement in order to make informed financial decisions. This involves thoroughly checking that:
Typically performed by auditors, lenders, or fraud prevention departments, bank statement verification determines whether the document accurately reflects the account activities.
This is crucial for establishing trust in statements used as financial or income proof, as well as checking that accounts have not been compromised.
Stringent statement verification is key for security, compliance, and risk reduction across banking, accounting, lending, investments and other financial sectors.
Thorough bank statement verification is critical for companies across banking, accounting, lending, investments, insurance, and legal services in order to ensure financial integrity, compliance, and protect themselves from financial fraud.
It’s often done during the bank statement audit or bank statement analysis process to ensure the authenticity of the documents.
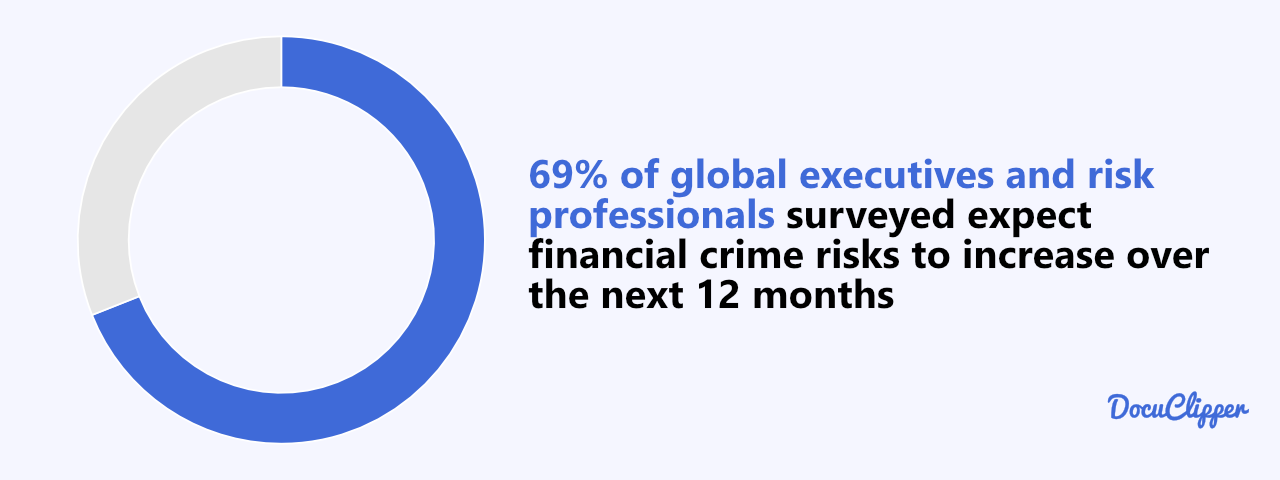
As the financial crimes are increasingly affect many different companies, it’s important to protect themselves.
69% of global executives and risk professionals surveyed expect financial crime risks to increase over the next 12 months with cybersecurity and data breaches as the primary drivers, followed by financial pressures on organizations.
Key reasons this process matters include:
Essentially, careful bank statement verification enables businesses across financial sectors to reduce risk, uphold security protocols, comply with regulations, validate reporting, and protect their interests.
And 74% companies plan to invest in technology to fight the likely increase in financial crime.

Performing a thorough bank statement verification requires scrutinizing the document in detail using the following guiding steps:
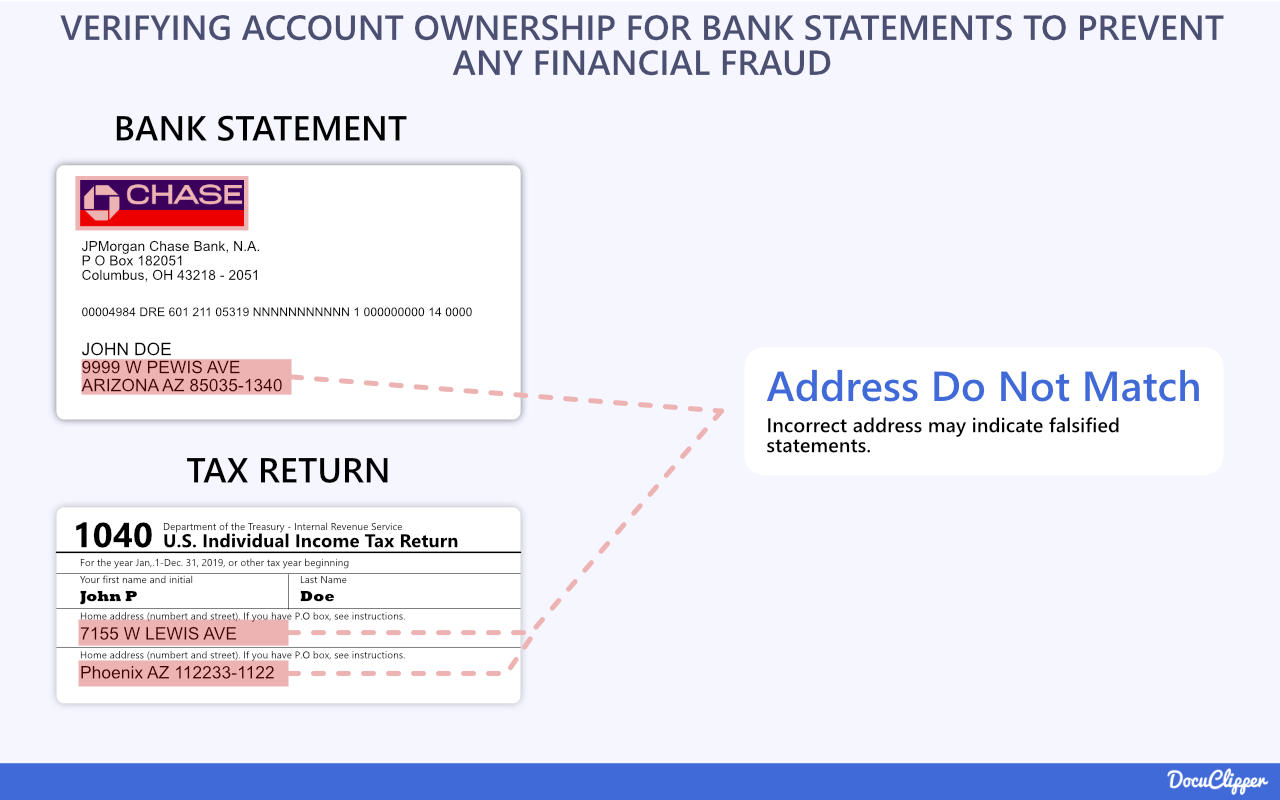
The first step in verifying a bank statement is to confirm ownership by the named account holder.
Cross check that key details – the account holder’s full name, account number, address, contact information – match across the statement and other financial documents provided.
Also verify these align correctly to the individual or business said to own the account. Look for mismatches in spellings, numbers transposed, or other discrepancies that may indicate falsified statements.
You can also ask for micropayment/micro-transaction for bank account verification.
Confirming all identifying information on the statement belongs to the purported owner is essential for validating authenticity and preventing financial fraud.
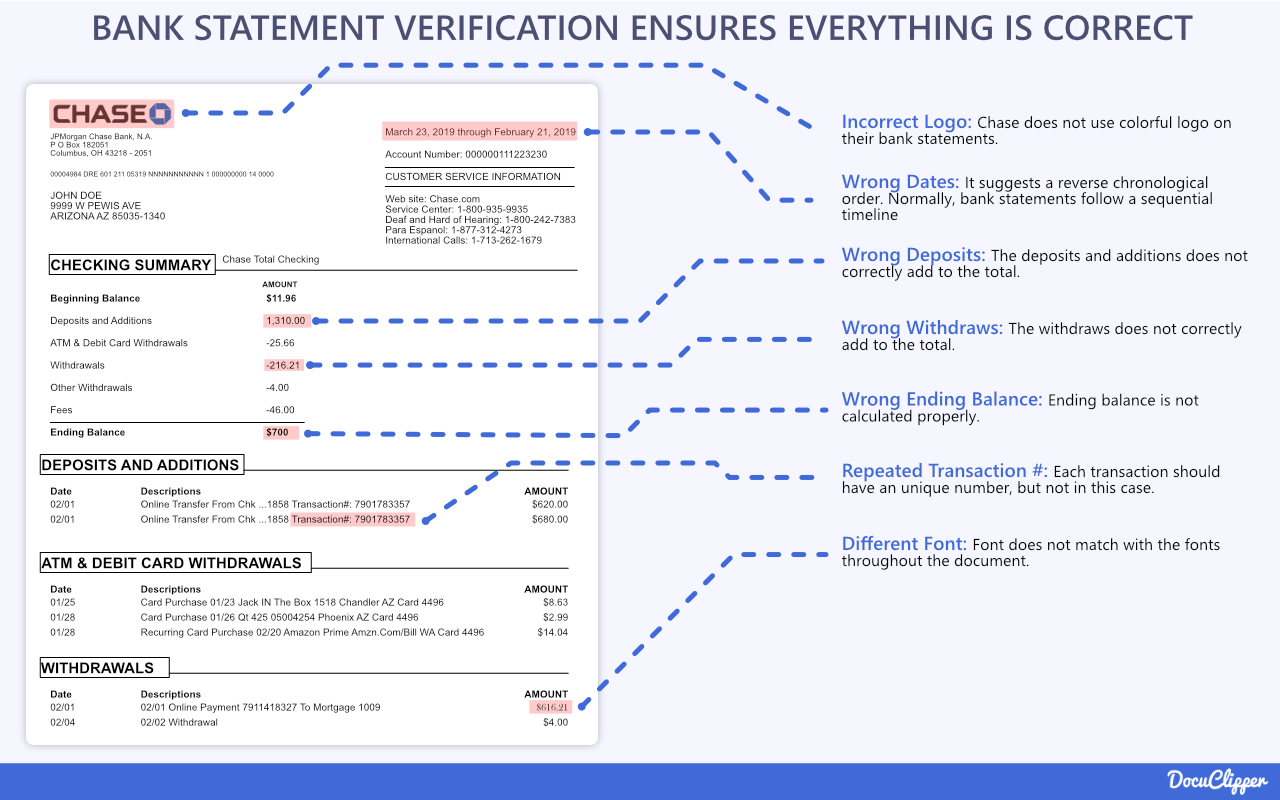
Carefully analyzing the bank statement for any signs of alteration, manipulation, or forgery. Look for inconsistencies in fonts, formatting, logos, paper quality or alignment that may indicate cut-and-paste editing.
Statements downloaded online can still be falsified then printed. Review line spacings for crowding or spreading which can show edited entries.
Also, verify print quality – clear digital copies can suggest manipulated files rather than originals.
If any entries or identifying details look tampered with or digitally altered, it warrants further verification with the issuing bank directly or rejecting the statement outright as unreliable proof.
For all this, the best way to ensure the bank statement is not faked is to ask for certified bank statements.
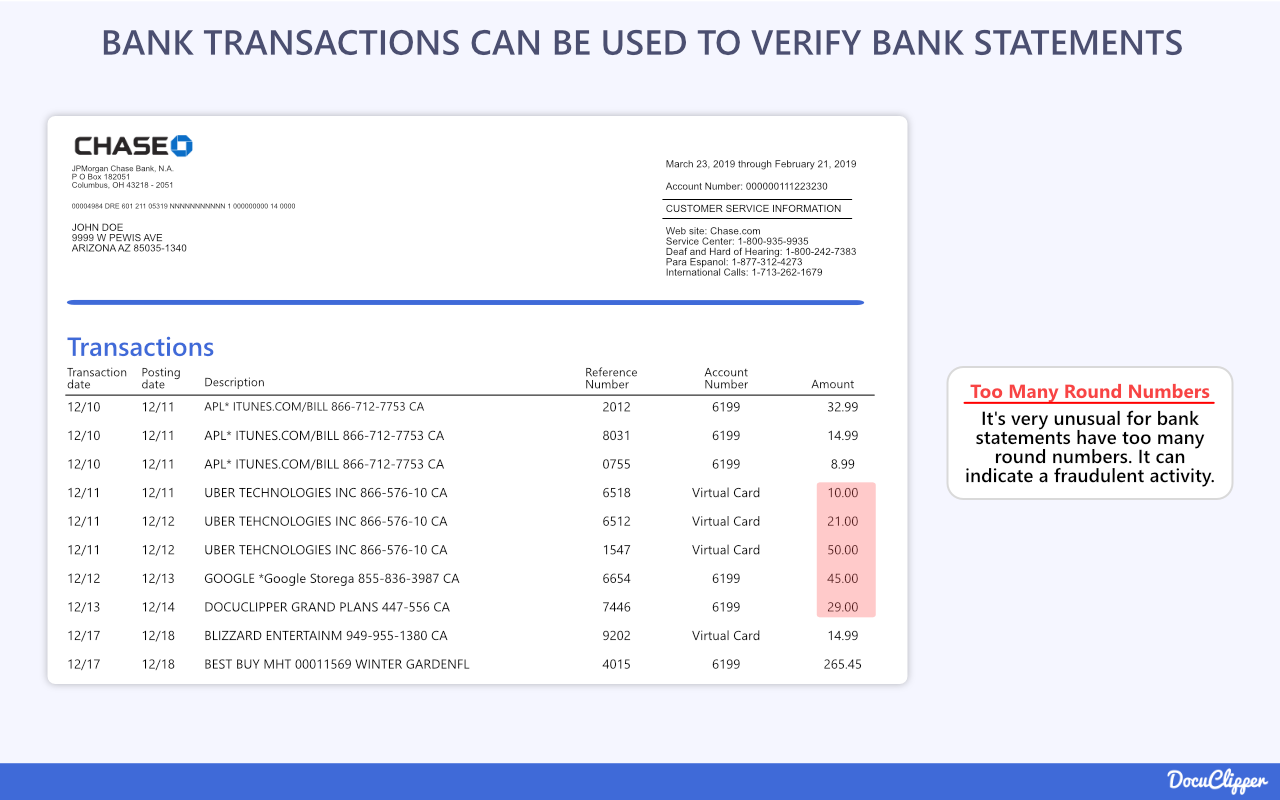
Reviewing the actual transactions on a statement is as crucial as checking totals. Scan activity patterns for odd repetitions, too many round numbers, gaps, or suspicious payments that could indicate manipulation.
Verify any exceptionally large credits or debits with the account holder or documents. Assess whether spending habits align to the entity’s expected behavior.
Analyzing the granular transaction flows reveals falsification more readily than solely matching totals.
It’s also good to know the bank statement abbreviations in order to recognize any bank transactions within the bank statement.
Compare key statement details against related documents like tax returns, invoices, payment receipts, and current bank records.
Check that names, dates, amounts paid or deposited, account numbers, balances owed, and more match accurately across these financial touchpoints.
Any discrepancies in payees, figures, or details between a statement and cross-referenced docs should prompt further verification to rule out fraudulent alterations.

Carefully note, cross-check, and confirm all credits and debits on the statement reflect valid transactions, free of manipulation.
Trace withdrawals to cancelled checks, wire approvals, or other withdrawal verification notices to validate accuracy.
Deposits should align to check images, deposit slips, electronic payments received or other validating formats documenting the credit’s authenticity.
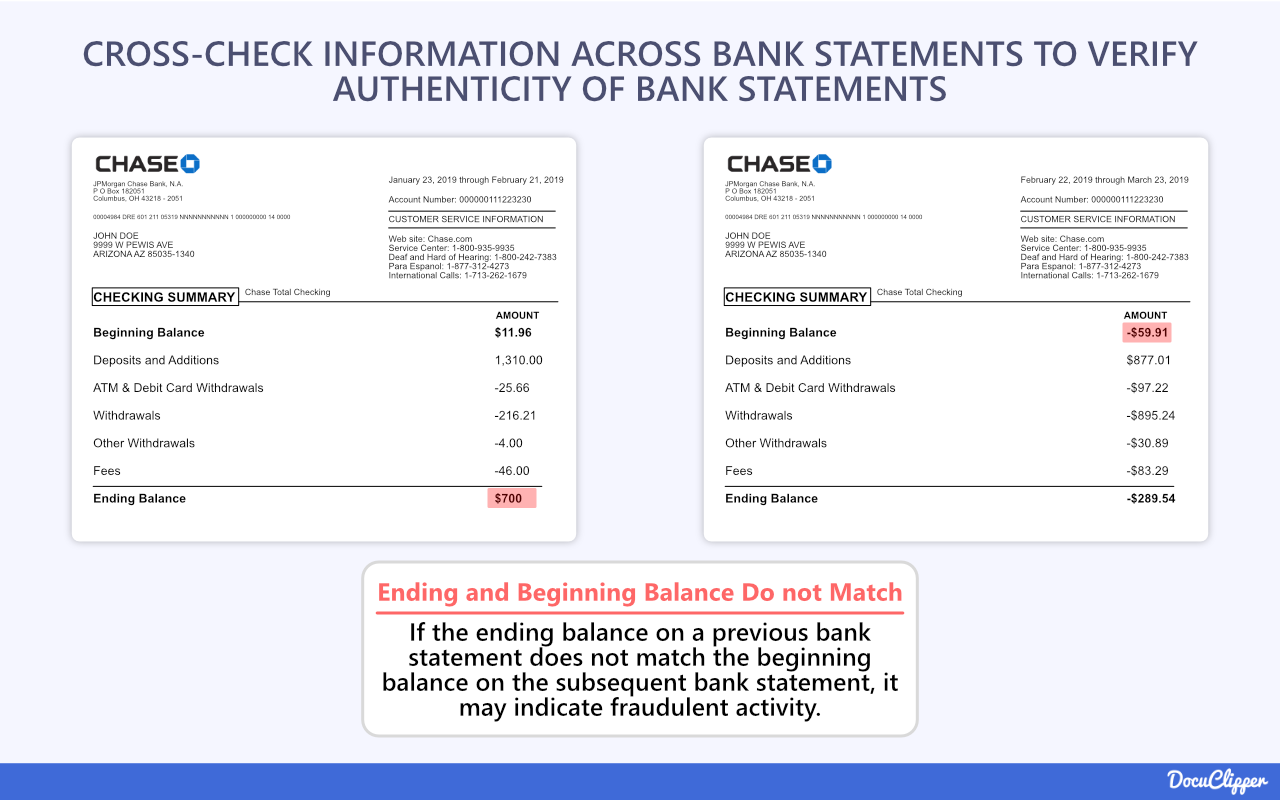
Verify balances carry over accurately across consecutive statements. Match the ending balance from one statement to beginning balance on the next statement.
This consistency check helps facilitate bank statement reconciliation by identifying potentially manipulated or missing pages in a statement file.
It assists in cross-verifying that no unexplained balance changes or discrepancies exist across the statement period timeline.
Any such inaccuracies between statement time periods indicate issues needing further investigation directly through the bank to rule out potential fraud or reporting errors before completing bank statement reconciliation.
Verify logos, stamps, watermarks, and the bank’s contact information conform to official branding and details confirmed directly with the financial institution. Fake bank statements often contain incorrect fonts, colors, or info. Even slight deviations could betray inauthentic documents.
If any statement details remain unverified or suspicious after due diligence review, make direct contact with the issuing bank branch to validate accuracy.
Discuss any questionable activity, substitutions, balance issues and validate legitimacy of stamps or logos.
Getting bank confirmation of details and statement veracity provides the utmost proof against potential fraud.
Advanced technologies now automate and streamline the bank statement verification process to catch subtle indicators of fraud such as:
This key technological capability enables companies such as lenders, financial institutions, or even accountants to quickly verify any bank statement and get detailed information on any possible fraudulent activities.
These technologies are saving millions of dollars and in the rise of financial crime, they’re becoming even more crucial.
In fact, 51% of surveyed organisations say they experienced fraud in the past two years, the highest level in our 20 years of research.

With that, here are some of the important modern technologies to verify bank statements:
OCR assists verification by electronically extracting important text and data of both scanned and born-digital bank statements – including main identifiers, transaction descriptions, dates, amounts, account numbers, logos, and more.
Using an OCR bank statement converter makes verification easier as any discrepancies within the transactions can easily be highlighted.
It facilitates efficient analysis by enabling:
The textual data parsing and structured data comparison powers of OCR provide a vital boost to bank statement verification efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models strengthen verification through advanced pattern recognition across statement datasets including:
Applied alongside human intelligence, AI and ML techniques equip investigators to quickly analyze larger bank statement volumes to accurately determine statement integrity, escalating higher risk documents for further diligence while clearing statements validated by the algorithms.

Digital forensics provides crucial tools for further validating e-statements through analysis like:
When statements pass initial integrity checks, experts can corroborate legitimacy further through examining delicate underlying code for any evidence of manipulation.
While most falsified documents alter content visibly, digital forensics ensures even stealthier edited statements don’t slide through undetected.
Thorough bank statement verification is crucial across lending, investing, insurance, law, and other financial services for security, compliance, and risk reduction.
While advancing technologies and fraud sophistication pose challenges, following best practices around multi-point checks, cross-referencing documents, transaction analysis, and directly contacting banks aids statement integrity confirmation.
Keeping verification processes robust yet empathetic ensures both customer trust and institutional interests stay protected from falsified financial reporting.
Here are answers to all the frequently asked questions about bank statement verification:
The purpose is to authenticate that bank statements are valid and unaltered through extensive checking of details like names, figures, dates, account numbers against other documents and directly with the bank. This mitigates fraud risk.
Compare transactions like withdrawals and deposits against images of cleared checks, wire approvals, deposit slips, or other corroborating documents that validate the transaction details through an additional source.
Verifying involves cross-checking statement details against other financial documents, scrutinizing statement formatting for anomalies, confirming account ownership ties back to the customer, contacting the bank directly, and potentially leveraging technologies like OCR, AI and digital forensics to automate analysis.
Advanced technologies like OCR, AI, ML, and digital forensics aid experts in automating time-consuming manual checks, recognizing subtle anomalies, and efficiently pinpointing areas needing further verification.
Keep an eye out for logos, headers, or identifying details that don’t match a bank’s official documentation. Also look for blurred text, misalignments, weird spacings, or font differences indicating potential manipulation.